Vertical Scaling
Get more RAM, processors, disks for one machine, but you will exhaust the financial resources/state.
Horizontal Scaling
Plural number of machines, use multiple servers to build the topology.
Cache
.html
Requires a lot of work when want to update/redesign the page.
MySQL Query Cache
query_cache_type = 1
Memcached
Store whatever you want in RAM.
Garbage Collection: expire objects based on when they are put in.
Load Balancing
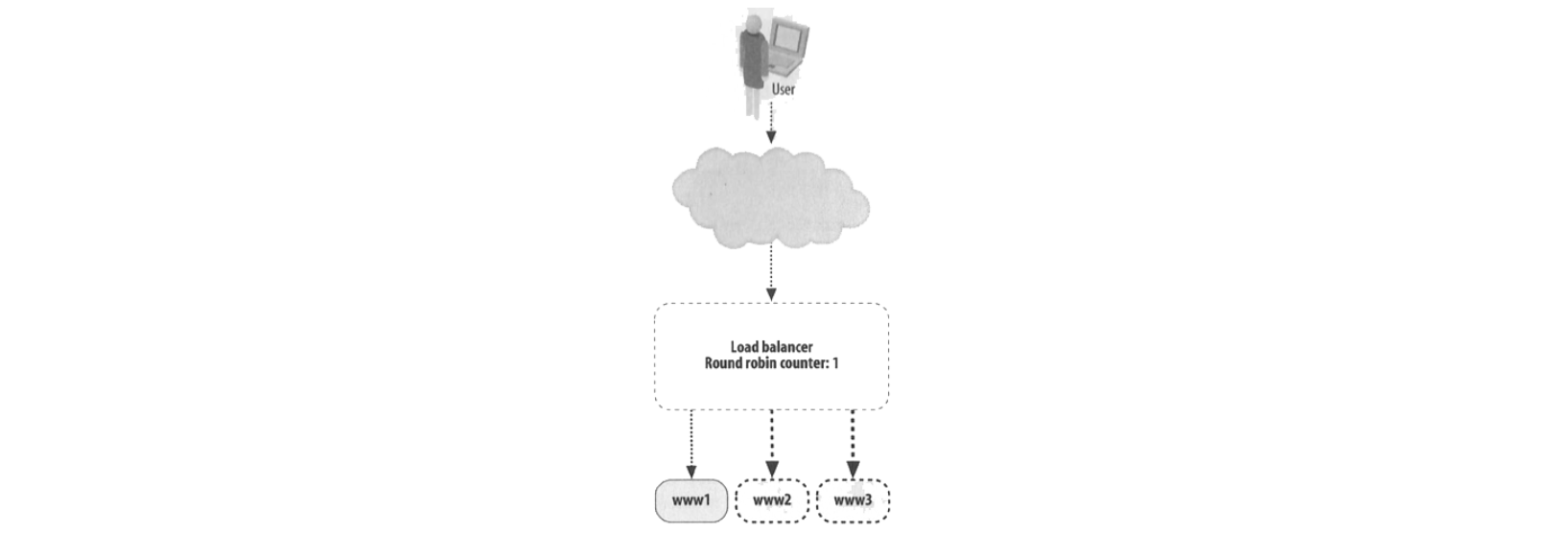
Implementation
- Dedicated servers for images, videos… for different host HTTP header.
- Round Robin. The load balancer can be a DNS setup which returns the IP address of server 1 when the first time someone asks for a URL, then return the IP address of server 2 when the second time someone asks for the same url, then server 3, server 4… eventually wrapping up.
- Downside: one server may get a really computational heavy user.
- Based on the load on a server.
- Have a server specifically for storing sessions. But what if that machine breaks down. Lacks redundancy, can add RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks).
Load Balancers

Replication
Master-Slave
Master: the main database that you write/read data to/from.
Slave: anytime a query is executed on the master that same query is copied down to one or more slaves and they do the exact same thing.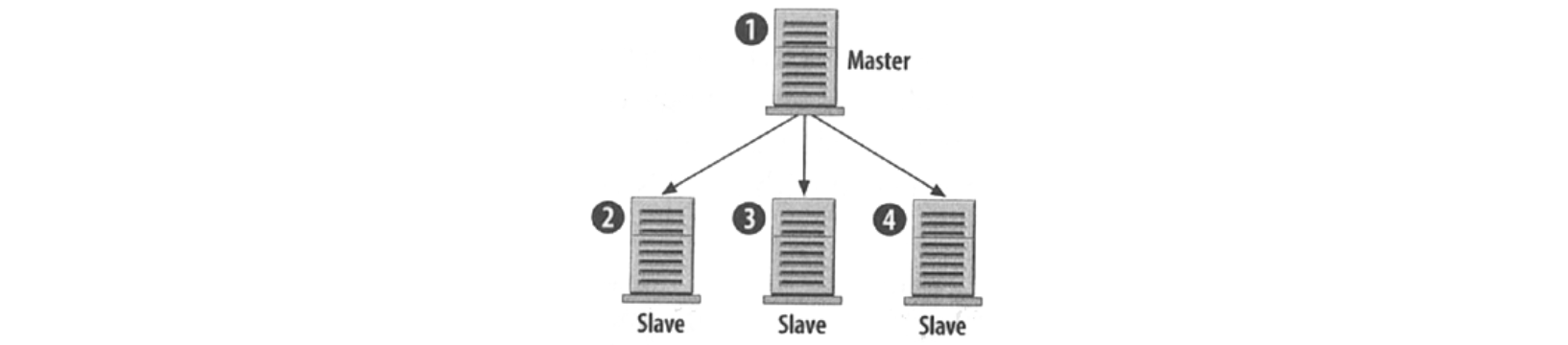
Advantage
- If the master is down, promote one of the slaves and do some configuration. (redundancy)
- If there are a lot queries, you could just load balance across database servers.
- For read heavy websites, any
selectcan go to all four databases, while anyinsert/update/deletehas to go to server master.
Master-Master
You could write to either server one or two and if you happen to write to server 1 that query gets replicated on server 2 and vice versa, so now you could keep it simple.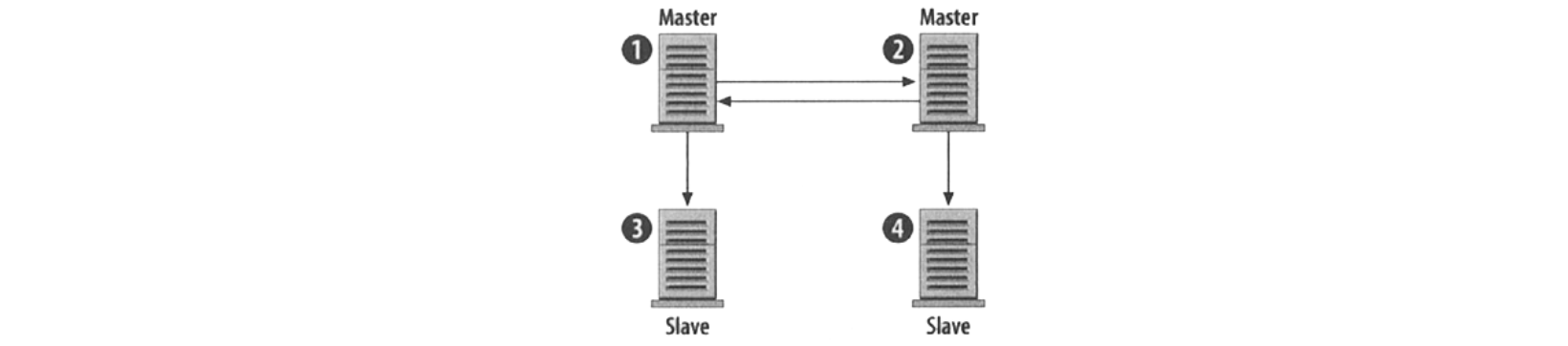
Load Balancing + Replication
active + passive pair of load balancers, passive promote itself when receives no more packets from the active one, and send packets to each other.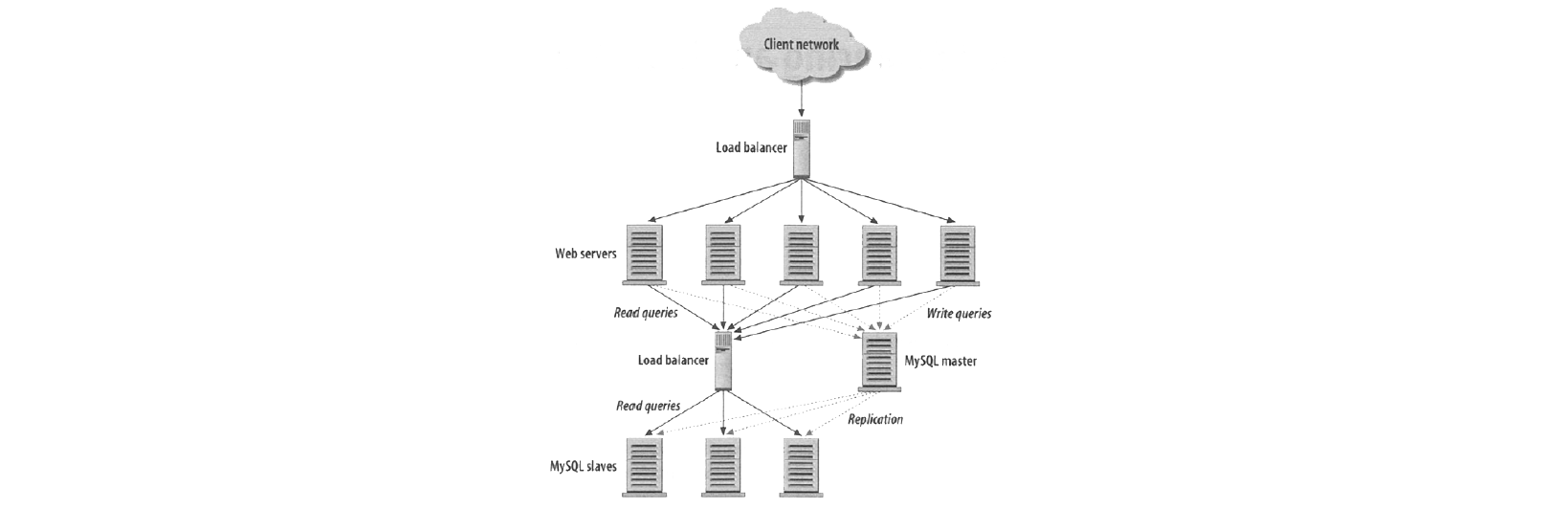
Partitioning
A-M cluster and N-Z cluster: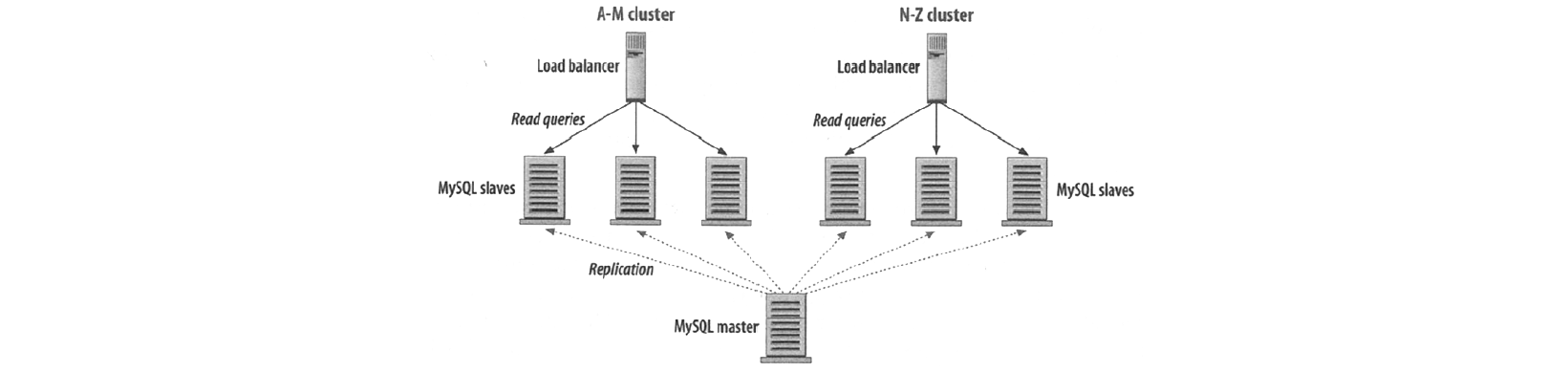
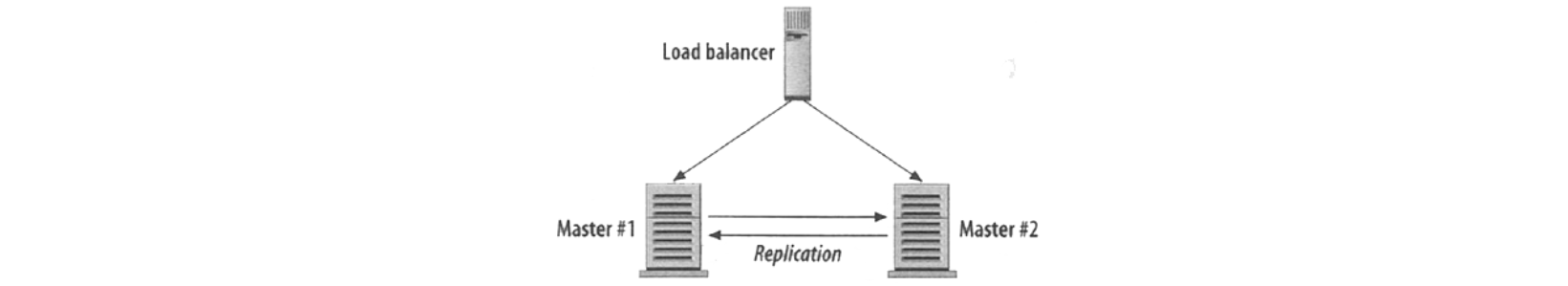
High Availability
One load balancer, two master replicating each other: