四两拨千斤的位运算,比如:剥离最右边的 1、将最右边的 1 置 0 等等。更多技巧可以参考 Low Level Bit Hacks。
Bitwise XOR returns 0 (false) if both bits are the same and returns 1 (true) otherwise. In other words, it only returns 1 if exactly one bit is set to 1 out of the two bits in comparison: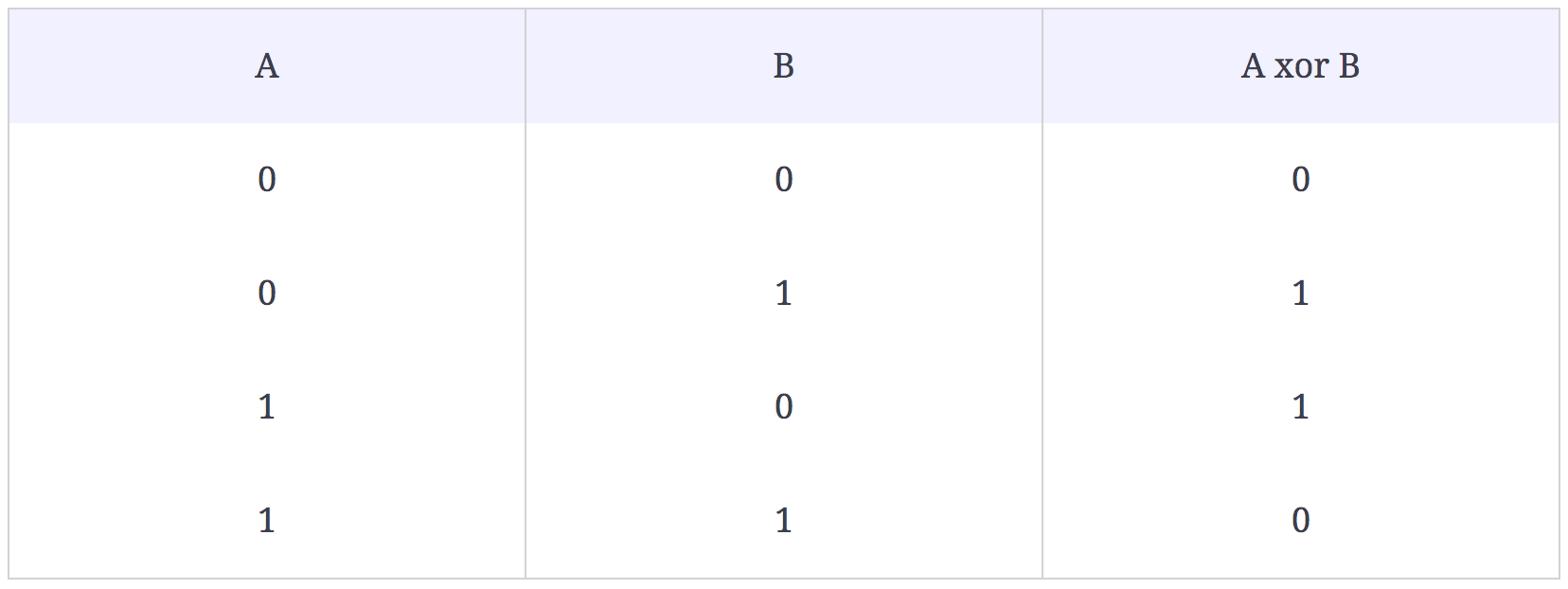
It is surprising to know the approaches that the XOR operator enables us to solve certain problems. For example, let’s take a look at the following problem:
Given an array of n-1 integers in the range from 1 to n, find the one number that is missing from the array.
Example:
1 | Input: 1, 5, 2, 6, 4 |
A straight forward approach to solve this problem can be:
- Find the sum of all integers from 1 to n; let’s call it: s1.
- Subtract all the numbers in the input array from s1; this will give us the missing number.
This is what the algorithm will look like:
1 | def find_missing_number(nums): |
Time & Space Complexity: The time complexity of the above algorithm is O(n) and the space complexity is O(1).
While finding the sum of numbers from 1 to n, we can get integer overflow when n is large.
Remember the important property of XOR that it returns 0 if both the bits in comparison are the same. In other words, XOR of a number with itself will always result in 0. This means that if we XOR all the numbers in the input array with all numbers from the range 1 to n then each number in the input is going to get zeroed out except the missing number. Following are the set of steps to find the missing number using XOR:
- XOR all the numbers from 1 to n, let’s call it: x1.
- XOR all the numbers in the input array, let’s call it: x2.
- The missing number can be found by x1 XOR x2.
Here is what the algorithm will look like:
1 | def find_missing_number(nums): |
Time & Space Complexity: The time complexity of the above algorithm is O(n) and the space complexity is O(1). The time and space complexities are the same as that of the previous solution, but, in this algorithm, we will not have any integer overflow problem.
Following are some important properties of XOR to remember:
- Taking XOR of a number with itself returns 0, e.g.,
- 1 ^ 1 = 0
- 29 ^ 29 = 0
- Taking XOR of a number with 0 returns the same number, e.g.,
- 1 ^ 0 = 1
- 29 ^ 0 = 29
- XOR is Associative & Commutative, which means:
- (a ^ b) ^ c = a ^ (b ^ c)
- a ^ b = b ^ a
Snippets
1 | n1xn2 = 0 |
LeetCode
136. Single Number
260. Single Number III
476. Number Complement
832. Flipping an Image