四两拨千斤的位运算,比如:剥离最右边的 1、将最右边的 1 置 0 等等。更多技巧可以参考 Low Level Bit Hacks。
Bitwise XOR returns 0 (false) if both bits are the same and returns 1 (true) otherwise. In other words, it only returns 1 if exactly one bit is set to 1 out of the two bits in comparison: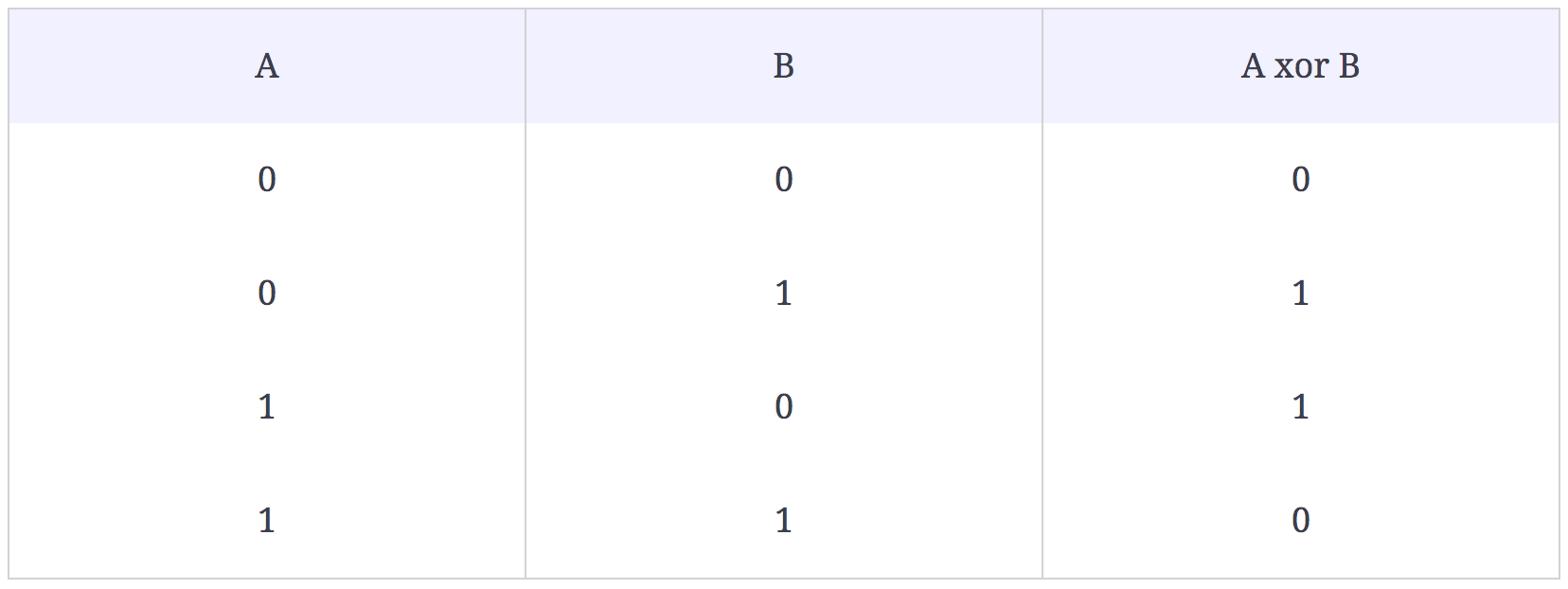
It is surprising to know the approaches that the XOR operator enables us to solve certain problems. For example, let’s take a look at the following problem:
Given an array of n-1 integers in the range from 1 to n, find the one number that is missing from the array.
Example:
1 | Input: 1, 5, 2, 6, 4 |
A straight forward approach to solve this problem can be:
- Find the sum of all integers from 1 to n; let’s call it: s1.
- Subtract all the numbers in the input array from s1; this will give us the missing number.