Introduction
This chapter presents the application developer’s view of SAP HANA. It gives an overview of both the programming languages for writing code that runs inside SAP HANA, and the client libraries used by client applications to connect to SAP HANA.
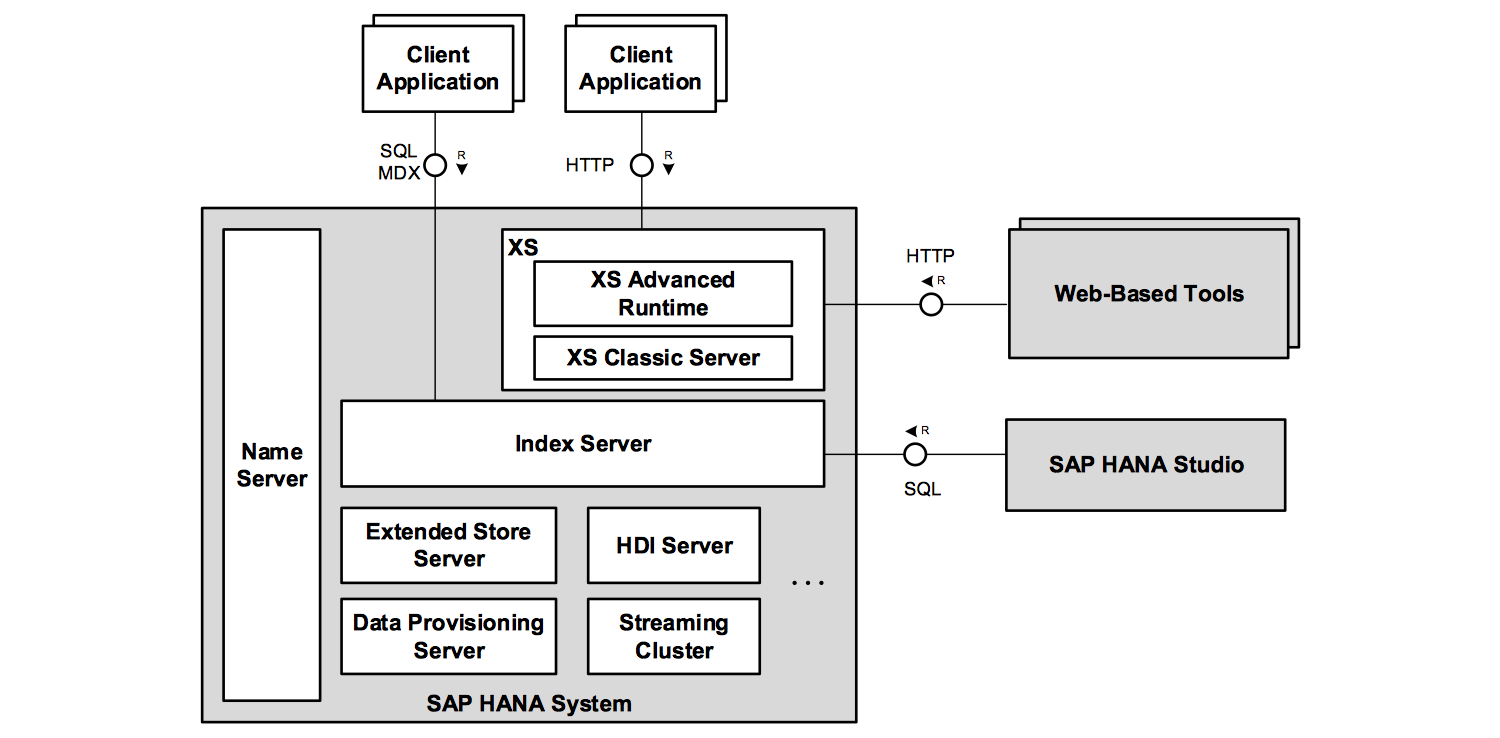
Database applications use well-defined interfaces to communicate with the database management system functioning as a data source, usually over a network connection.
The application, often running in the context of an application server, takes the role of a client, while the database system plays the role of a server. Client applications typically use vendor-supplied client libraries which implement part of the API and encapsulates the communication details.
The leading programming language for database application is the SQL. SQL provides functional capabilities for creating, accessing, maintaining, controlling, and protecting relational data.
SAP HANA greatly extends SQL. This includes SAP HANA-specific SQL statements, views, data types, and the possibility to write Procedures in several languages, such as SQLScript, L, C++ and R.Modeled Views are design-time abstractions that allow developers to work efficiently with SAP HANA’s extended views on a higher level of abstraction.
An alternative query language for clients is MDX. Pioneered by Microsoft, MDX is used by applications to query OLAP (OnLine Analytical Processing) data models. Applications can query graph data with the openCypher query language and implement custom graph algorithms as graph stored procedures.